What is Docker?

In simpler words, Docker is a tool that allows developers, sys-admins etc. to easily deploy their applications in a sandbox (called containers) to run on the host operating system i.e. Linux.
The key benefit of Docker is that it allows users to package an application with all of its dependencies into a standardized unit for software development.
Unlike virtual machines, containers do not have high overhead and hence enable more efficient usage of the underlying system and resources.
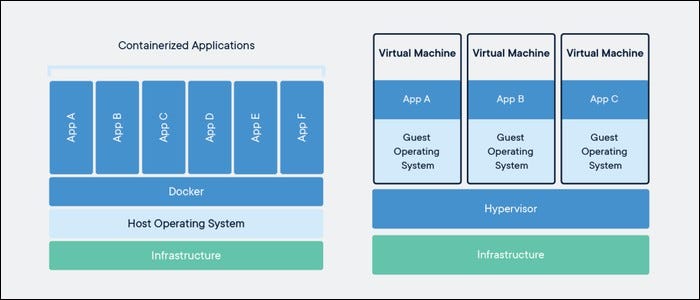
Docker runs containers, which use the same host operating system, and only virtualize at a software level.
Docker Engine runs on Linux, Windows, and macOS, and supports Linux and Windows for Docker containers.
What is Dockerfile?
A Dockerfile is the recipe to build a Docker image. This is the workflow: first you create a Dockefile, then you built a Docker image from it using docker build, and finally you run a container from the image. A Dockerfile is a text file with instructions on how to build an image. Those instructions are part of a configuration language, which includes keywords like FROM, LABEL, RUN, COPY, ENTRYPOINT, CMD, EXPOSE, ENV and more.
Example Dockerfile
Let’s say you have a folder with a simple Node.js app composed by an app.js, a package.json file that lists a couple dependencies you need to install before running the app, and package-lock.json.
FROM node:14
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
COPY package*.json app.js ./
RUN npm install
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "app.js"]
Details please go to Dockerfile 1 and Dockerfile 2.
Learn Docker in 5 days !!!
Day1-General Concepts Day2-Basic Commands Day3-Sotrage and Networks Day4-Dockerfiles Day5-Docker compose
Playing with Docker
pullthe image from docker registry
docker pull busybox- list images
docker images - run a docker container based on
busyboximage
docker run busybox echo "hello from busybox - show running containers
docker ps
docker ps -adocker container ls - go into a docker container
docker run -it busybox sh
Since Docker creates a new container every time, everything will be rebuilt again in each instance.
docker runmultiple times and leaving stray containers will eat up disk space.docker rmto clean up containers.
docker rm contain-ID
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q -f status=exited)
-q: return numeric ID
-f: filters output based on conditions provided
docker container prunecan be used to remove all the stopped containers.- to delete docker images
docker rmi - Build a container from an image and remove it when it exits.
docker run --rm image
docker run -d -P --name xxx image
-d: will detach terminal
-p: publish all exposed port to random ports
--name: container name we want to give - Check the ports, then open
http://localhost:portin browser.
docker port xxx - to stop a detached container
docker stop xxx
Terminology
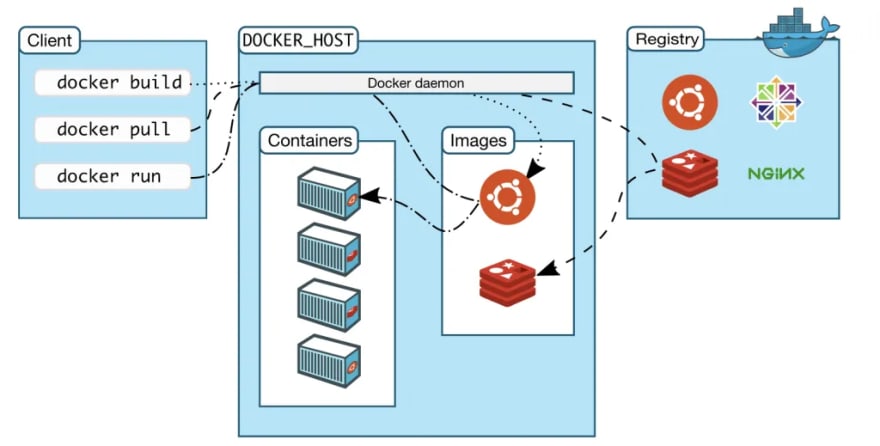
Images: the blueprints form the basis of containers.Containers: created from docker images and run the actual application.Docker Daemon: the background service running on the host that manage building, running and distributing docker containers.Docker Client: The command line tool that allows the user to interact with the daemon.Docker Hub: A registry of docker images.
Docker Images
Docker images are the basis of containers. To see the list of images that are available locally, use the docker images command.
How to build an image
git clonedokcer repocd docker-curriculum/flask-app- make
Dockerfile: a simple text file that contains a list of commands that the Docker client calls while creating an image. - create docker image from a
Dockerfile
docker build -t test/flask .-t: optional tag name - run the image
How To Remove Docker Images, Containers, and Volumes?
- To clean up any resources — images, containers, volumes, and networks — that are dangling (not associated with a container)
docker system prune - To additionally remove any stopped containers and all unused images (not just dangling images), add the
-aflag to the command
docker system prune -a - More usages, can go to here
Reference
- Docker Containers 101
- Docker curriculum
- How to write a docker file
- Doker for beginners
- What does Docker do, and when should you use it?
- Getting Started with Docker for Developers
- How to remove docker images, containers and volumes
- How to remove Docker Images, Containers and Volumes
- How to share data between docker containers